
In the ever-evolving world of finance and technology, Bitcoin stands as a revolutionary innovation that has transformed how we perceive and use money. Since its inception in 2009, Bitcoin has grown from an obscure digital experiment into a global phenomenon, attracting investors, technologists, and financial experts alike.
But what exactly is Bitcoin? Why has it garnered so much attention? And how does it work?
In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore what Bitcoin is, how it works, its history, benefits, risks, and why it might be one of the most important inventions of the 21st century.
1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows people to send and receive money over the internet without relying on a bank or government. It operates on a technology called blockchain, which is a public ledger of all transactions made on the network.
Bitcoin is:
- Digital – It exists only in electronic form.
- Decentralized – No single authority controls it.
- Peer-to-Peer – Users can send it directly to each other.
- Limited in supply – Only 21 million bitcoins will ever be created.
Bitcoin was introduced in 2008 by an anonymous person (or group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto through a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”
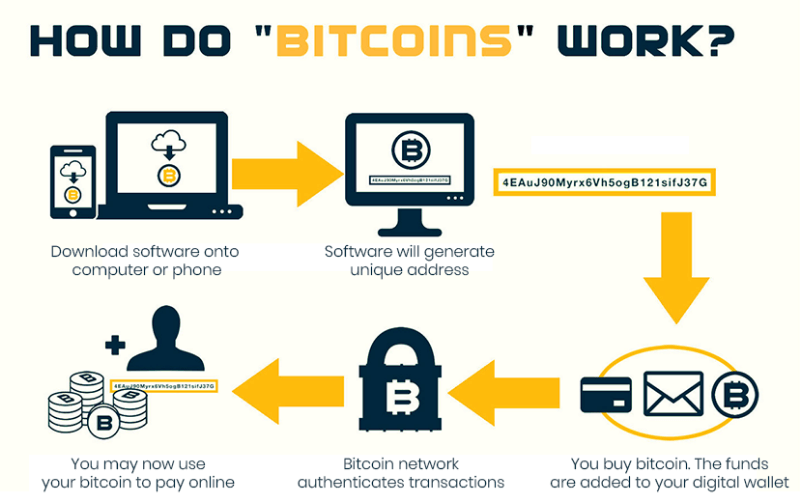
2. How Does Bitcoin Work?
At the heart of Bitcoin is the blockchain. This is a distributed database maintained by a network of computers (called nodes) around the world.
Here’s how it works:
a. Transactions
When someone sends bitcoin to another person, the transaction is broadcasted to the Bitcoin network.
b. Mining
Miners (specialized computers) collect these transactions and group them into a “block”. They then solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate the block. This process is called Proof of Work.
c. Blockchain
Once validated, the block is added to the chain of previous blocks—hence, the blockchain. This record is permanent and cannot be altered.
d. Security
Bitcoin’s security comes from the massive computational power of miners and the decentralized structure of the network.
3. The History of Bitcoin
- 2008: The Bitcoin whitepaper is published by Satoshi Nakamoto.
- 2009: The first block (Genesis Block) is mined.
- 2010: First real-world Bitcoin transaction—10,000 BTC for two pizzas.
- 2013-2017: Bitcoin gains popularity, hitting $1,000, then $10,000.
- 2021: Bitcoin reaches an all-time high of over $60,000.
- Today: Bitcoin is traded globally, accepted by some companies, and seen as “digital gold.”
4. Why Bitcoin is Important
a. Financial Freedom
Bitcoin enables individuals to have full control over their money, without the need for banks or governments.
b. Inflation Protection
With only 21 million bitcoins that can ever exist, it acts as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
c. Borderless Transactions
Bitcoin can be sent anywhere in the world within minutes and with relatively low fees.
d. Inclusion
People in countries with weak banking infrastructure can access Bitcoin through a mobile phone and an internet connection.
5. Benefits of Using Bitcoin
- Fast Transactions: Much faster than traditional banking, especially for international payments.
- Lower Fees: Especially when compared to credit cards or wire transfers.
- Transparency: All transactions are public and can be verified on the blockchain.
- Privacy: Users can transact without revealing personal information.
- Ownership: You control your own money—no bank can freeze your Bitcoin wallet.
6. Risks and Challenges
Despite its advantages, Bitcoin comes with certain risks:
a. Volatility
Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate dramatically. This makes it risky for short-term investments or use as a daily currency.
b. Regulatory Issues
Governments around the world are still figuring out how to regulate Bitcoin, which can impact its usage.
c. Scams and Fraud
Since Bitcoin is pseudonymous and irreversible, it has been used in scams. Users must be cautious.
d. Technical Understanding
Using Bitcoin securely requires a basic understanding of how it works and how to store it safely.

7. How to Get Started with Bitcoin
If you’re interested in Bitcoin, here are a few steps to get started:
- Get a Bitcoin Wallet: This can be a mobile app, hardware wallet, or desktop program.
- Buy Bitcoin: You can purchase through crypto exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, WazirX, etc.
- Secure Your Wallet: Use strong passwords, 2FA, and backup your keys.
- Stay Informed: Follow trusted crypto news sources and communities.
8. Common Myths About Bitcoin
- “Bitcoin is anonymous” – It’s actually pseudonymous. All transactions are public but not directly tied to real names.
- “Bitcoin is only for criminals” – While it’s been used in illicit activities, so has cash. Most Bitcoin users are legitimate.
- “It has no real value” – Bitcoin’s value comes from scarcity, decentralization, security, and market demand.
- “It will be banned” – Some countries have restricted it, but others (like the U.S., Germany, Japan) are embracing it with regulations.
9. The Future of Bitcoin
The future of Bitcoin is still being written. Some possible directions:
- Mainstream Adoption: More businesses and countries may start accepting Bitcoin.
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin is increasingly seen as a store of value like gold.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like the Lightning Network are making Bitcoin faster and more scalable.
- Regulation and Integration: Governments may create frameworks to integrate Bitcoin into the financial system.